What Is The Reason for The Bearing Noise
- Share
- Issue Time
- Oct 9,2022
Summary
Excitation caused by changes in the number of loading rolling bodies When a radial load is loaded on a certain bearing, the number of its load-bearing rolling bodies will change slightly in the operation, causing the deviation of the load direction.
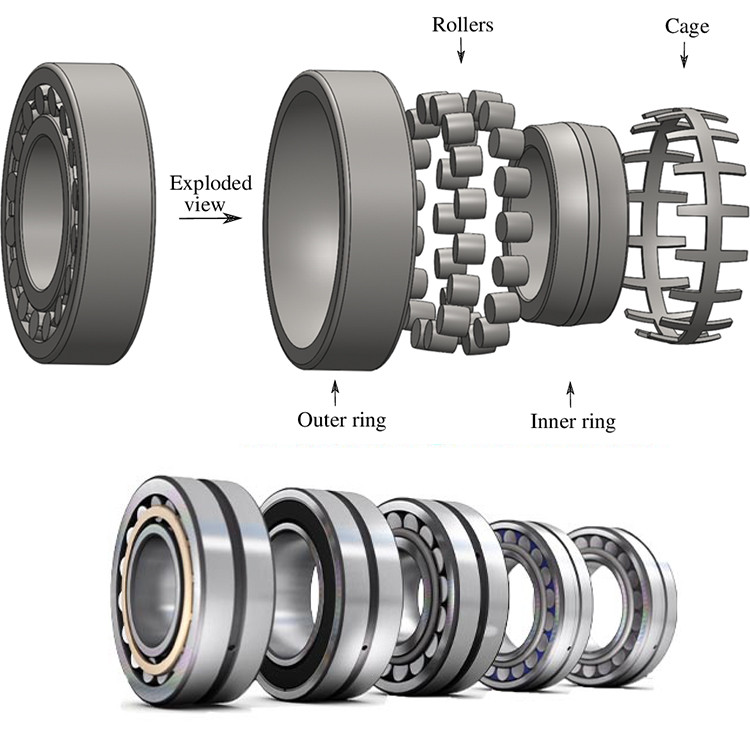
1. Excitation caused by changes in the number of loading rolling bodies When a radial load is loaded on a certain bearing, the number of its load-bearing rolling bodies will change slightly in the operation, causing the deviation of the load direction.
2. Local damage A small number of bearing rollers and rolling bodies may be damaged due to operation or installation errors. In operation, the damaged bearing components will produce a specific vibration frequency. Vibration frequency analysis can identify the damaged bearing components. This principle has been applied to state monitoring equipment to monitor bearing damage.
3. Precision of related components In the case of close cooperation between the bearing inner and outer ring and the bearing seat or transmission shaft, the inner and outer ring of the bearing may be deformed by improper cooperation with the shape of the adjacent components. If deformation occurs, vibration and noise may occur during operation.
4. Pollutants If the equipment is operating in a polluted environment, the impurities may enter the bearing rolling body to produce a vibration sound. This situation can usually hear a disturbing noise.
5. The reasons for noise from other rolling bearings are complicated. One is the surface wear of the inner and outer rings of the bearings. This wear, damaged the bearing and shell, bearing and shaft coordination relationship, causing the axis to deviate from the correct position. The shaft produces an abnormal sound when moving at a high speed.
In addition, insufficient bearing lubrication, the formation of dry friction, and bearing crushing will produce abnormal sounds. Bearing wear, holder loose, and damage will also produce abnormal sounds.

The different noise sizes of the bearings are different?
1. Low noise ratio of ball bearings, low roller bearings, and low (friction) noise of bearings with less sliding are lower than bearings with more sliding; those with more balls, thick outer ring, and less noise;
2. The noise of using the physical holder bearing is relatively lower than that of the bearing using the stamping holder
3. The noise of the plastic holder bearings is lower than that of the above two kinds of holders;
4. Bear with high precision, especially those with higher accuracy of a rolling body, have relatively less noise than that of low precision bearings;
5. The noise of small bearings is relatively less than that of large bearings.
Of course, this theory is so, there are many factors to affect the size of noise in practical application.
30 reasons for the bearing ringing
1. Oil has impurities;
2. Retainer fracture;
3. Bearing roller path will rust;
4. Bearing noise (with external vibration source interference);
5. The ring roller lane is unqualified (factory problem);
6. The bearing swimming gap is too small or too large (the factory problem);
7. The diameter of the seat hole is too small (causing the bearing temperature is too high);
8. Seal ring is eccentric (encounter adjacent parts and have friction);
9. There is debris in the bearing seat hole (residual debris, dust particles, etc.);
10. The noise of the bearing (caused by the end surface of the roller or the steel ball skid);
11. The shaft shoulder is too large (touch the bearing seal and have friction);
12. The gap of the labyrinth seal ring is too small (friction with the shaft);
13. Trending of lock washer (touch the bearing and friction);
14. The shoulder of the seat hole is too large (distorting the seal on the bearings);
15. The position of the oil ring is not appropriate (touch the flange and friction);
16. Mix sand particles or carbon particles in the bearing to play the role of the abrasive agent;
17. Steel ball and roller path wear (unqualified grinding or product collision);
18. The thermal elongation of the shaft is too large (the bearing is subject to static axial additional load);
19. The bearing is flattened by the seat hole (the roundness of the seat hole is not good, or the seat hole is not straight);
20. Bearing mixed with water, acid or paint and other dirt, play a corrosive role;
21. The coordination between the bearing and shaft is too loose (the diameter of the shaft is small or the tightening sleeve is not tight);
22. The swimming gap of the bearing is too small and too tight when rotating (the tightening set spin is too tight);
23. There is a pressure pit on the steel ball or roller (caused by the hammer beating the bearing for installation);
24. The bearing is heated and deformed (caused by removing the bearing with a spray gun);
25. The shaft is too thick to make the actual fit too tight (causing too high bearing temperature or noise);
26. Insufficient lubrication (oil level is too low, improper storage of oil or fat through sealing leakage);
27. The cushion of the bottom surface of the bearing seat is uneven (resulting in deformation of the seat hole and even cracks in the bearing seat);
28. The bearing seat hole diameter is too large, and the actual fit is too loose (the bearing temperature is too high, the outer ring skid);
29. The bearing seat hole becomes larger (the bearing seat hole of nonferrous metal is enlarged, or enlarged due to thermal expansion);
30. Additional bearing load (poor axial bearing, or two fixed-end bearings on one shaft)